Many poorly-known small mammals have remained undetected for decades. It’s not all doom and gloom though: a recent scientific paper “Continued survival of the elusive Seram orange melomys (Melomys fulgens)” documents that a species previously unrecorded since 1920 appears to be surviving on the island of Seram, Indonesia. Hopefully this is good news not just for this species, but for other ‘Lost’ mammals of Seram.
The paper is co-authored by two of the SMSG core team- Prof. Sam Turvey (ZSL) and Dr Ros Kennerley (Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust) and describes evidence of the survival of Melomys fulgens, a distinctive orange murid. M. fulgens is one of five endemic rodents described from Seram, known only from their first official descriptions – some of which date back to over a century ago – and having remained undetected in surveys ever since.
The evidence for the survival of the Seram Orange Melomys in the latest research paper comes from expeditions in 1993 and 1994, plus a more recent study of local ecological knowledge in 2017.
1993/94 expeditions
Two trips to the island were made during these years and three individuals of the species were captured, proving that the species was extant in the 1990s.

Melomys fulgens in a cage. Credit: K. Leus

Melomys fulgens in cage. Photo credit: National Museums Scotland
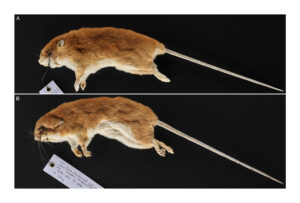
Melomys fulgens specimens. Photo credit: National Museums Scotland.
Using Local Ecological Knowledge
In 2017 interviews took place with people in six villages along Seram’s north coast. The questionnaire asked about people’s knowledge of local wildlife and forest activities and the results provided valuable insights into the fauna and how people use the landscape. Excitingly, several respondents said that they had seen the species in the previous months and recent years.
What does this mean for its conservation?
Findings indicate relatively widespread distribution of M. fulgens in coastal forest across Seram, including sites adjacent to Manusela National Park (see map), with local suggestions that it occurs throughout the lowland forest zone to its upper elevational limit. This means that using the limited known localities and continuing loss of Seram’s lowland forest, we propose a new Red List assessment of Vulnerable. The next steps are to work with local NGOs to consider conservation actions to help bolster the species.
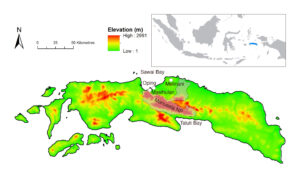
Map of Seram, showing collection
locations of Melomys fulgens specimens and
reports (white circles), and boundary of Manusela National
Park.
This rediscovery not only raises hope for the continued survival of Seram’s other ‘lost’ mammals and tropical small mammal diversity in general, but also demonstrates the importance of local ecological knowledge in detecting distinctive species in poorly-studied regions.
To find out more about Re:wild’s Lost Species click here.
Do you have a Lost small mammal you’d like to search for?
If so, please click here to contact us.





